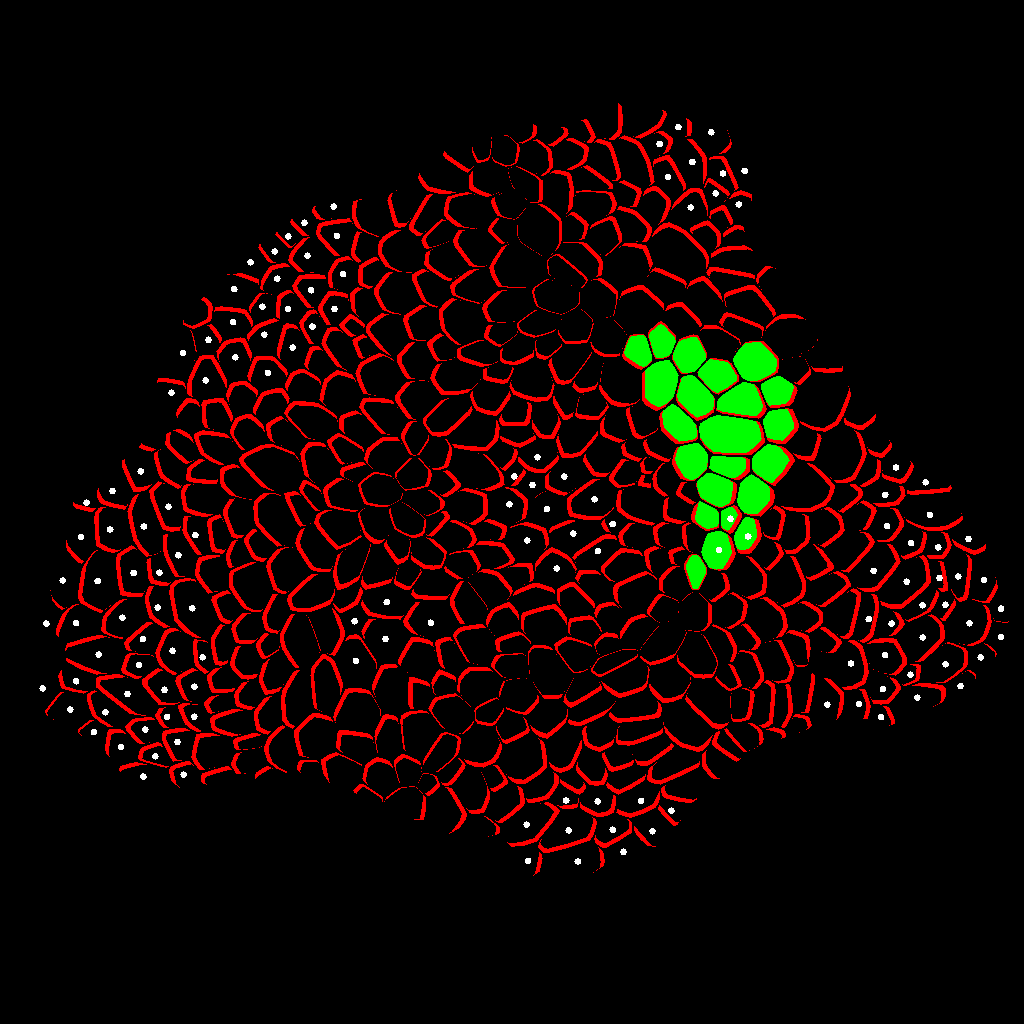
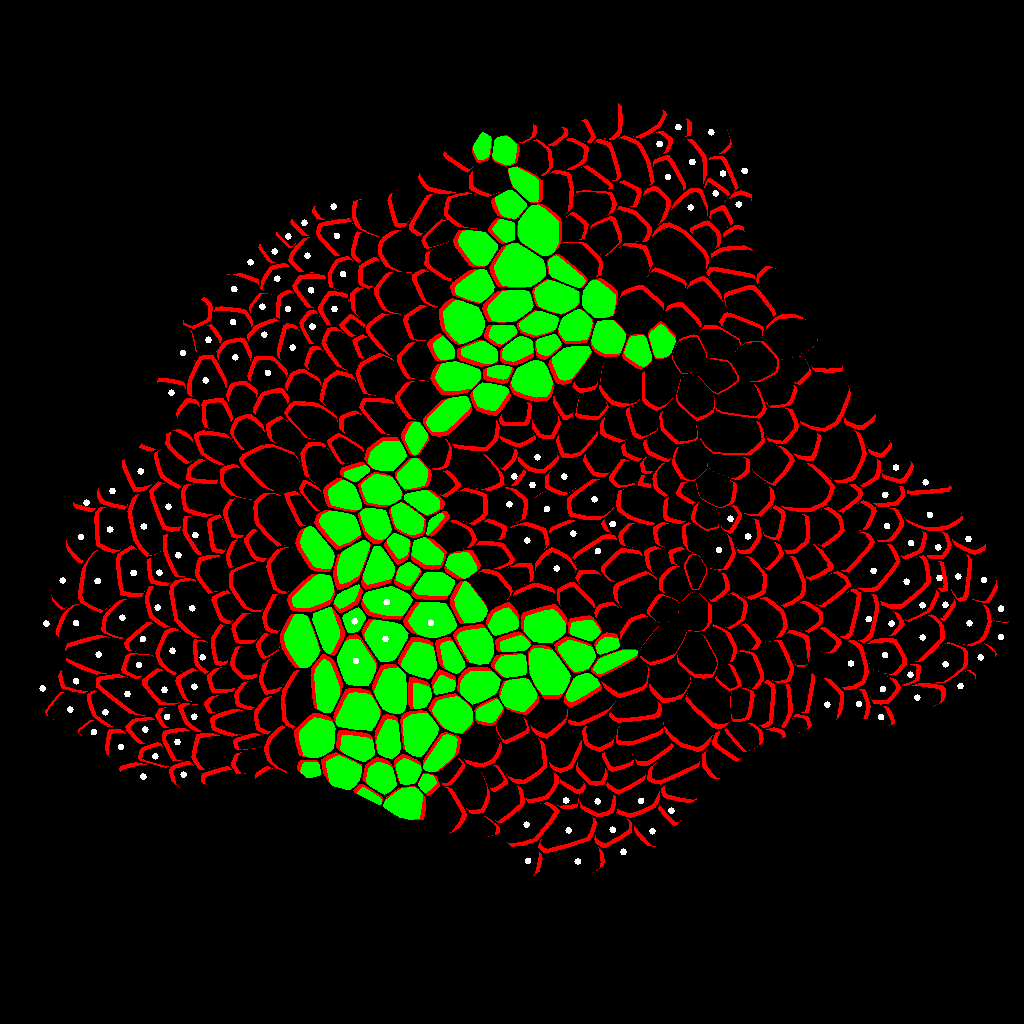
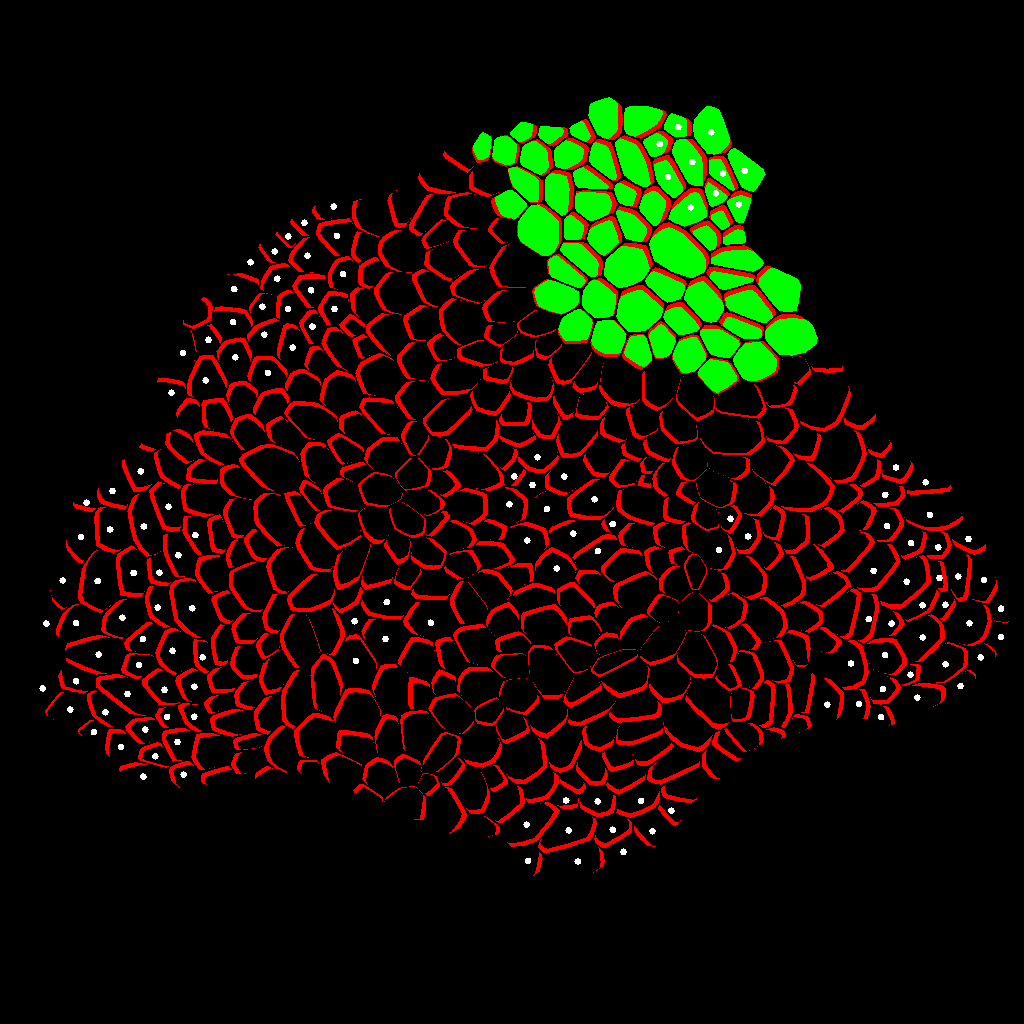
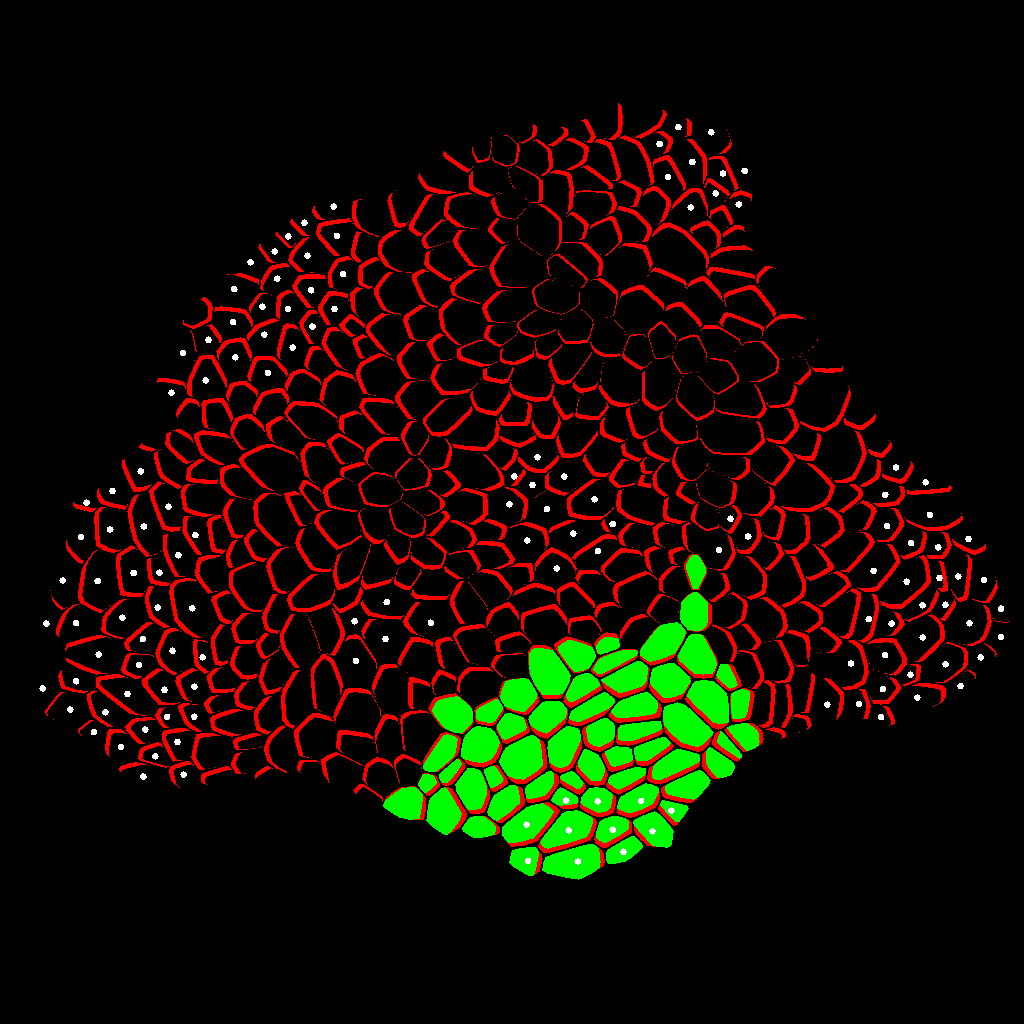
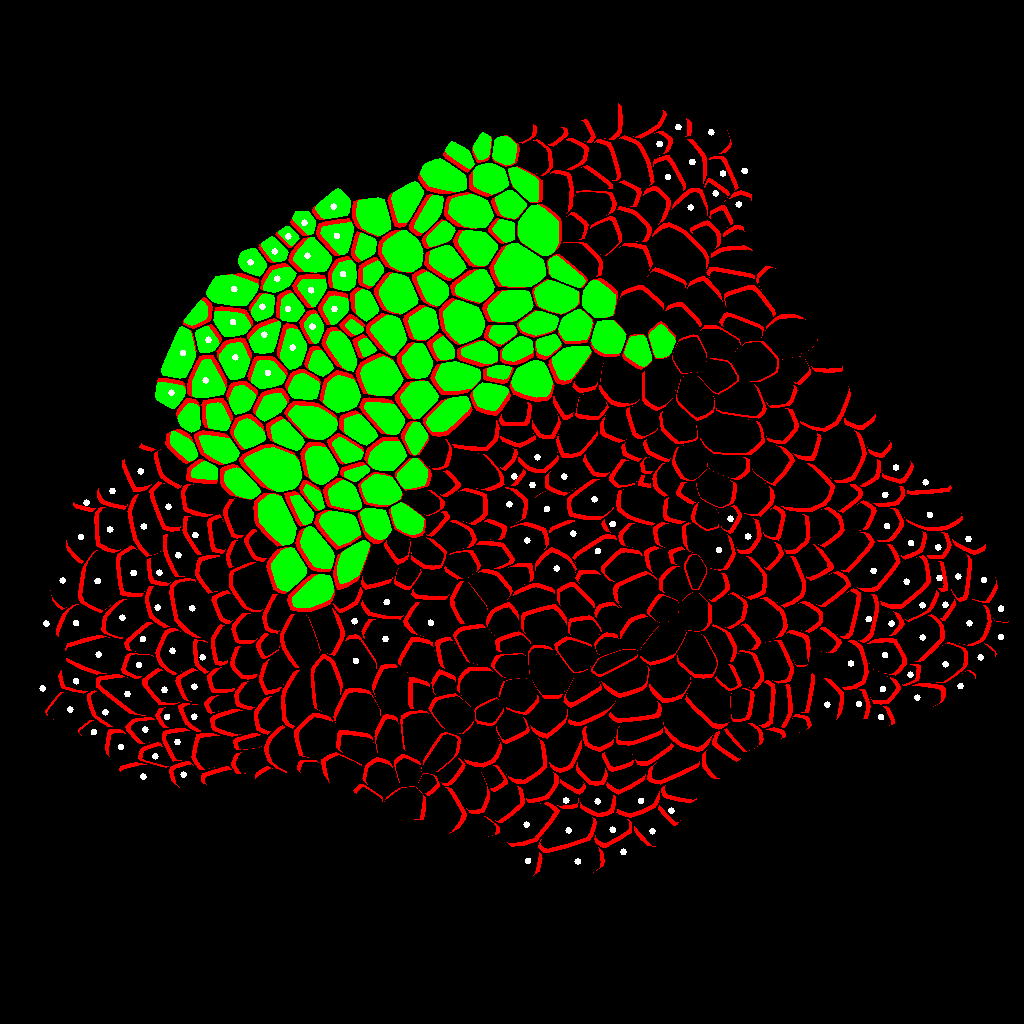
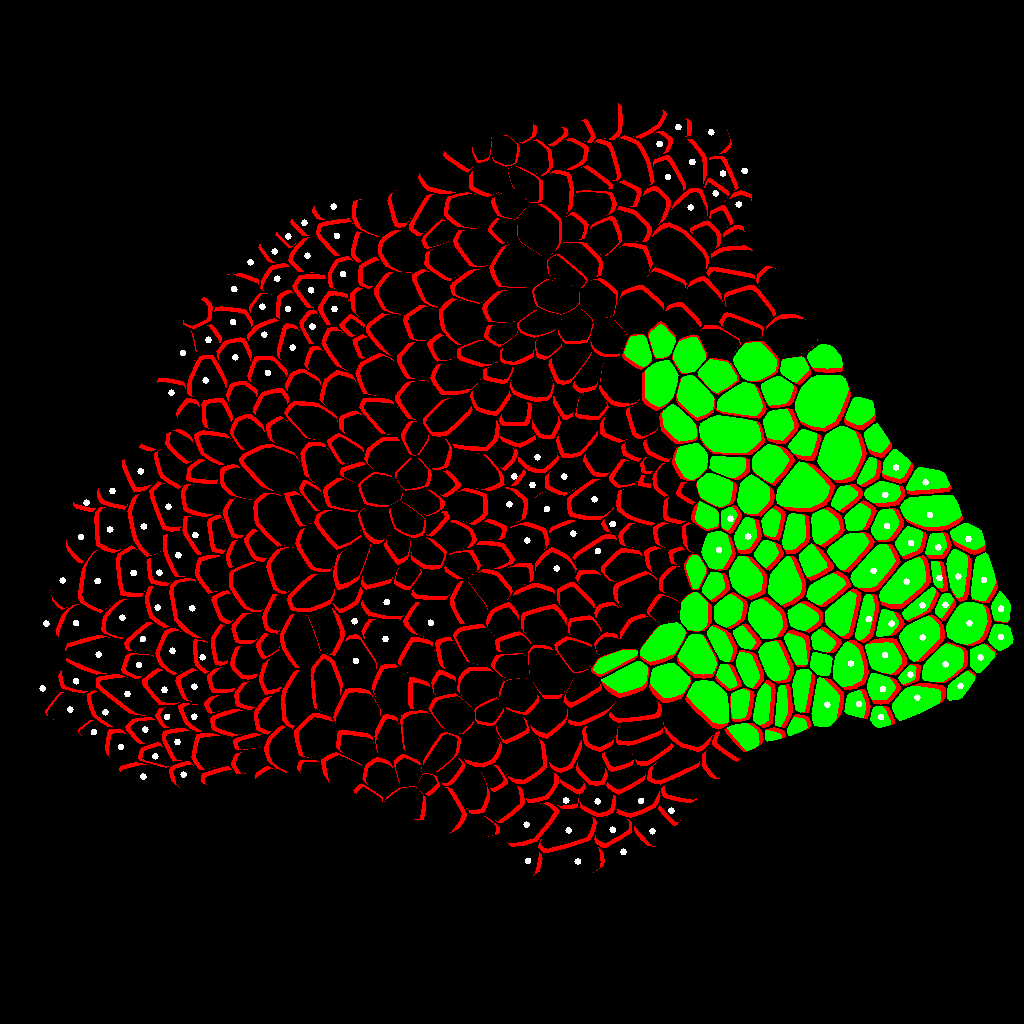
Zone Analysis
Another use of the built in framework tools might be a structural analysis of cellular networks. In this case, the previously presented example (wt_tutorial_03.py) is used to acquire the tissue. Then the connected fragments of the tissue are found with the following function:
def set_influence_zones( wt, **keys):
def f( wt, directed_cell_edge ):
return wt.directed_cell_edge_property( directed_cell_edge, "PIN")
from openalea.stse.structures.algo.walled_tissue_influence_zones import set_property_on_tissue_component
for i in regions2cells:
#print zones[ i ]
for j in regions2cells[ i ]:
set_property_on_tissue_component( wt=wt,
cell= j,
f_component=f,
tol=0.1,
property=i+"_IZ",
property_value=1.,
with_neighbors=False,
fill_gaps=False,
additional_vertices=[])
def f( wt, directed_cell_edge ):
return wt.directed_cell_edge_property( directed_cell_edge, "PIN")
from openalea.stse.structures.algo.walled_tissue_influence_zones import set_property_on_tissue_component
for i in regions2cells:
#print zones[ i ]
for j in regions2cells[ i ]:
set_property_on_tissue_component( wt=wt,
cell= j,
f_component=f,
tol=0.1,
property=i+"_IZ",
property_value=1.,
with_neighbors=False,
fill_gaps=False,
additional_vertices=[])
Then the specific display can be used for presenting the tissue components:
def f_pin( wt ):
"""Function returning function which returns the membrane thickness according
to PIN cell_edge property.
<Long description of the function functionality.>
:parameters:
wt : `WalledTissue`
Tissue containing cell data
:rtype: function
:return: Function which returns the membrane thickness according
to PIN cell_edge property.
"""
f1 = f_property2scalar( wt_property_method=wt.directed_cell_edge_property,
property = "PIN",
default_value = 0.,
segment = (0, 1),
factor = 1.)
def f( cell, edge ):
try:
ce = wv_edge2cell_edge( wt, edge )
if ce[ 1 ] == cell: ce=(ce[1],ce[0])
v = f1( ce )
except TypeError:
v = f1( None )
return v
return f
# sample visualization using plantGL
def vis( wt, config, props=[], clear=False, save=False ):
"""Displaying of IZ and saving the results.
"""
for prop in props:
if clear: pd.SCENES[ pd.CURRENT_SCENE ].clear()
pd.instant_update_viewer()
visualisation_pgl_2D_varried_membrane_thickness( wt,
abs_intercellular_space=0.05,
abs_membrane_space=0.25,
stride=20,
f_membrane_thickness = f_pin( wt ),
f_cell_marking = [f_cell_marking( properties=config.cell_regions.keys(), property_true_radius=0.2)],
f_material = f_properties2material( [prop] ),
reverse = True
)
pd.instant_update_viewer()
if save: pgl.Viewer.frameGL.saveImage( config.file_folder+"/"+"iz"+prop+".png" )
"""Function returning function which returns the membrane thickness according
to PIN cell_edge property.
<Long description of the function functionality.>
:parameters:
wt : `WalledTissue`
Tissue containing cell data
:rtype: function
:return: Function which returns the membrane thickness according
to PIN cell_edge property.
"""
f1 = f_property2scalar( wt_property_method=wt.directed_cell_edge_property,
property = "PIN",
default_value = 0.,
segment = (0, 1),
factor = 1.)
def f( cell, edge ):
try:
ce = wv_edge2cell_edge( wt, edge )
if ce[ 1 ] == cell: ce=(ce[1],ce[0])
v = f1( ce )
except TypeError:
v = f1( None )
return v
return f
# sample visualization using plantGL
def vis( wt, config, props=[], clear=False, save=False ):
"""Displaying of IZ and saving the results.
"""
for prop in props:
if clear: pd.SCENES[ pd.CURRENT_SCENE ].clear()
pd.instant_update_viewer()
visualisation_pgl_2D_varried_membrane_thickness( wt,
abs_intercellular_space=0.05,
abs_membrane_space=0.25,
stride=20,
f_membrane_thickness = f_pin( wt ),
f_cell_marking = [f_cell_marking( properties=config.cell_regions.keys(), property_true_radius=0.2)],
f_material = f_properties2material( [prop] ),
reverse = True
)
pd.instant_update_viewer()
if save: pgl.Viewer.frameGL.saveImage( config.file_folder+"/"+"iz"+prop+".png" )
The final result is presented here: